Database normalization is a key process in designing efficient and reliable databases. It involves structuring data to minimize redundancy, prevent anomalies, and enhance data integrity. By breaking large tables into smaller, related ones, normalization ensures consistency and simplifies database management.
𝘽𝙚𝙣𝙚𝙛𝙞𝙩𝙨 𝙤𝙛 𝙉𝙤𝙧𝙢𝙖𝙡𝙞𝙯𝙖𝙩𝙞𝙤𝙣
1. 𝘙𝘦𝘥𝘶𝘤𝘦𝘴 𝘙𝘦𝘥𝘶𝘯𝘥𝘢𝘯𝘤𝘺 – Eliminates duplicate data, reducing storage costs and preventing inconsistencies.
2. 𝘌𝘯𝘩𝘢𝘯𝘤𝘦𝘴 𝘋𝘢𝘵𝘢 𝘐𝘯𝘵𝘦𝘨𝘳𝘪𝘵𝘺 – Prevents update, insertion, and deletion anomalies, ensuring data accuracy.
3. 𝘐𝘮𝘱𝘳𝘰𝘷𝘦𝘴 𝘘𝘶𝘦𝘳𝘺 𝘗𝘦𝘳𝘧𝘰𝘳𝘮𝘢𝘯𝘤𝘦 – Well-structured databases enable faster and more efficient data retrieval.
4. 𝘚𝘪𝘮𝘱𝘭𝘪𝘧𝘪𝘦𝘴 𝘔𝘢𝘪𝘯𝘵𝘦𝘯𝘢𝘯𝘤𝘦 – Data modifications in one table automatically reflect in related tables.
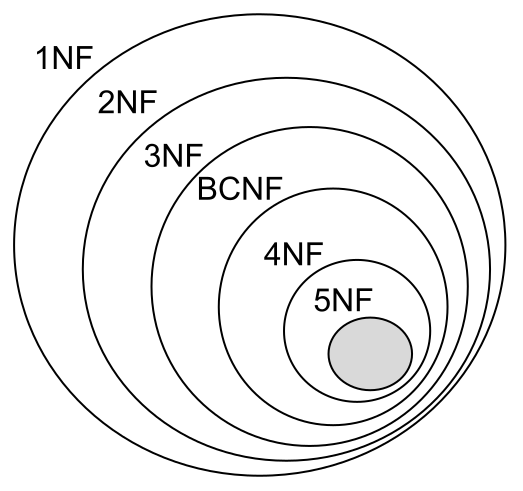
𝙉𝙤𝙧𝙢𝙖𝙡𝙞𝙯𝙖𝙩𝙞𝙤𝙣 𝙁𝙤𝙧𝙢𝙨
1. 𝘍𝘪𝘳𝘴𝘵 𝘕𝘰𝘳𝘮𝘢𝘭 𝘍𝘰𝘳𝘮 (1𝘕𝘍) – Ensures atomicity by eliminating duplicate columns and ensuring each column contains unique values.
2. 𝘚𝘦𝘤𝘰𝘯𝘥 𝘕𝘰𝘳𝘮𝘢𝘭 𝘍𝘰𝘳𝘮 (2𝘕𝘍) – Removes partial dependencies, ensuring non-key attributes depend entirely on the primary key.
3. 𝘛𝘩𝘪𝘳𝘥 𝘕𝘰𝘳𝘮𝘢𝘭 𝘍𝘰𝘳𝘮 (3𝘕𝘍) – Eliminates transitive dependencies, ensuring non-key attributes depend only on the primary key.
4. 𝘉𝘰𝘺𝘤𝘦-𝘊𝘰𝘥𝘥 𝘕𝘰𝘳𝘮𝘢𝘭 𝘍𝘰𝘳𝘮 (𝘉𝘊𝘕𝘍) – Strengthens 3NF by resolving cases where candidate keys create anomalies.
While normalization optimizes data integrity, excessive normalization may lead to performance issues due to complex joins. Striking a balance between normalization and denormalization is key to designing an efficient database system.